Different types of layer 2s
2023 Oct 31
See all posts
Different types of layer 2s
Special thanks to Karl Floersch for feedback and review
The Ethereum layer 2 ecosystem has been expanding rapidly over the
last year. The EVM rollup ecosystem, traditionally featuring Arbitrum, Optimism and Scroll, and more recently Kakarot and Taiko, has been progressing quickly,
making great strides on improving their security; the L2beat page does a good
job of summarizing the state of each project. Additionally, we have seen
teams building sidechains also starting to build rollups (Polygon), layer 1 projects
seeking to move toward being validiums (Celo), and totally new efforts (Linea, Zeth...). Finally,
there is the not-just-EVM ecosystem: "almost-EVMs" like Zksync, extensions like Arbitrum
Stylus, and broader efforts like the Starknet ecosystem, Fuel and others.
One of the inevitable consequences of this is that we are seeing a
trend of layer 2 projects becoming more heterogeneous. I expect this
trend to continue, for a few key reasons:
- Some projects that are currently independent layer 1s are
seeking to come closer to the Ethereum ecosystem, and possibly
become layer 2s. These projects will likely want a step-by-step
transition. Transitioning all at once now would cause a decrease in
usability, as the technology is not yet ready to put everything on a
rollup. Transitioning all at once later risks sacrificing momentum and
being too late to be meaningful.
- Some centralized projects want to give their users more
security assurances, and are exploring blockchain-based routes for doing
so. In many cases, these are the projects that would have
explored "permissioned consortium chains" in a previous era.
Realistically, they probably only need a "halfway-house" level of
decentralization. Additionally, their often very high level of
throughput makes them unsuitable even for rollups, at least in the short
term.
- Non-financial applications, like games or social media, want
to be decentralized but need only a halfway-house level of
security. In the social media case, this realistically
involves treating different parts of the app differently: rare and
high-value activity like username registration and account recovery
should be done on a rollup, but frequent and low-value activity like
posts and votes need less security. If a chain failure causes your post
to disappear, that's an acceptable cost. If a chain failure causes you
to lose your account, that is a much bigger problem.
A big theme is that while applications and users that are on
the Ethereum layer 1 today will be fine paying smaller but
still visible rollup fees in the short term, users from the
non-blockchain world will not: it's easier to justify paying
$0.10 if you were paying $1 before than if you were paying $0 before.
This applies both to applications that are centralized today, and to
smaller layer 1s, which do typically have very low fees while their
userbase remains small.
A natural question that emerges is: which of these complicated
tradeoffs between rollups, validiums and other systems makes sense for a
given application?
Rollups vs
validiums vs disconnected systems
The first dimension of security vs scale that we will explore can be
described as follows: if you have an asset that is issued on L1,
then deposited into the L2, then transferred to you, what level of
guarantee do you have that you will be able to take the asset back to
the L1?
There is also a parallel question: what is the technology choice that
is resulting in that level of guarantee, and what are the tradeoffs of
that technology choice?
We can describe this simply using a chart:
| Rollup |
Computation proven via fraud proofs or ZK-SNARKs, data stored on
L1 |
You can always bring the asset back to L1 |
L1 data availability + SNARK-proving or redundant execution to catch
errors |
| Validium |
Computation proven via ZK-SNARKs (can't use fraud proofs), data
stored on a server or other separate system |
Data availability failure can cause assets to be lost, but
not stolen |
SNARK-proving |
| Disconnected |
A separate chain (or server) |
Trust one or a small group of people not to steal your funds or lose
the keys |
Very cheap |
It's worth mentioning that this is a simplified schema, and
there are lots of intermediate options. For example:
- Between rollup and validium: a validium where
anyone could make an on-chain payment to cover the cost of transaction
fees, at which point the operator would be forced to provide some data
onto the chain or else lose a deposit.
- Between plasma and validium: a Plasma system offers
rollup-like security guarantees with off-chain data availability, but it
supports only a limited number of applications. A system could
offer a full EVM, and offer Plasma-level guarantees to users that do not
use those more complicated applications, and validium-level guarantees
to users that do.
These intermediate options can be viewed as being on a spectrum
between a rollup and a validium. But what motivates applications to
choose a particular point on that spectrum, and not some point further
left or further right? Here, there are two major factors:
- The cost of Ethereum's native data availability, which will
decrease over time as technology improves. Ethereum's next hard
fork, Dencun,
introduces EIP-4844 (aka
"proto-danksharding"), which provides ~32 kB/sec of onchain data
availability. Over the next few years, this is expected to increase in
stages as full
danksharding is rolled out, eventually targeting around ~1.3 MB/sec
of data availability. At the same time, improvements
in data compression will let us do more with the same amount of
data.
- The application's own needs: how much would users suffer
from high fees, versus from something in the application going
wrong? Financial applications would lose more from application
failures; games and social media involve lots of activity per user, and
relatively low-value activity, so a different security tradeoff makes
sense for them.
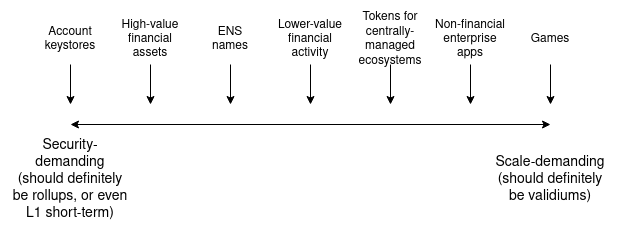
Approximately, this tradeoff looks something like this:
Another type of partial guarantee worth mentioning is
pre-confirmations. Pre-confirmations are messages
signed by some set of participants in a rollup or validium that say "we
attest that these transactions are included in this order, and the
post-state root is this". These participants may well sign a
pre-confirmation that does not match some later reality, but if they do,
a deposit gets burned. This is useful for low-value applications like
consumer payments, while higher-value applications like
multimillion-dollar financial transfers will likely wait for a "regular"
confirmation backed by the system's full security.
Pre-confirmations can be viewed as another example of a
hybrid system, similar to the "plasma / validium hybrid"
mentioned above, but this time hybridizing between a rollup (or
validium) that has full security but high latency, and a system with a
much lower security level that has low latency. Applications that need
lower latency get lower security, but can live in the same ecosystem as
applications that are okay with higher latency in exchange for maximum
security.
Trustlessly reading
Ethereum
Another less-thought-about, but still highly important, form of
connection has to do with a system's ability to read
the Ethereum blockchain. Particularly, this includes
being able to revert if Ethereum reverts. To see why
this is valuable, consider the following situation:
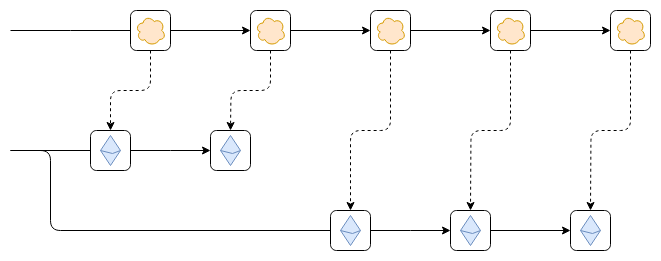
Suppose that, as shown in the diagram, the Ethereum chain reverts.
This could be a temporary hiccup within an epoch, while the chain has
not finalized, or it could be an inactivity
leak period where the chain is not finalizing for an extended
duration because too many validators are offline.
The worst-case scenario that can arise from this is as follows.
Suppose that the first block from the top chain reads some data from the
leftmost block on the Ethereum chain. For example, someone on Ethereum
deposits 100 ETH into the top chain. Then, Ethereum reverts. However,
the top chain does not revert. As a result, future blocks of the top
chain correctly follow new blocks from the newly correct Ethereum chain,
but the consequences of the now-erroneous older link (namely,
the 100 ETH deposit) are still part of the top chain. This exploit could
allow printing money, turning the bridged ETH on the top chain into a
fractional reserve.
There are two ways to solve this problem:
- The top chain could only read finalized blocks of
Ethereum, so it would never need to revert.
- The top chain could revert if Ethereum reverts.
Both prevent this issue. The former is easier to implement, but may
cause a loss of functionality for an extended duration if Ethereum
enters an inactivity leak period. The latter is harder to implement, but
ensures the best possible functionality at all times.
Note that (1) does have one edge case. If a 51% attack on Ethereum
creates two new incompatible blocks that both appear finalized at the
same time, then the top chain may well lock on to the wrong one (ie. the
one that Ethereum social consensus does not eventually favor), and would
have to revert to switch to the right one. Arguably, there is no need to
write code to handle this case ahead of time; it could simply be handled
by hard-forking the top chain.
The ability of a chain to trustlessly read Ethereum is valuable for
two reasons:
- It reduces security issues involved in bridging tokens issued on
Ethereum (or other L2s) to that chain
- It allows account abstraction wallets that use the shared keystore
architecture to hold assets on that chain securely.
- is important, though arguably this need is already widely
recognized. (2) is important too, because it means that you can have a
wallet that allows easy key changes and that holds assets across a large
number of different chains.
Does having a bridge
make you a validium?
Suppose that the top chain starts out as a separate chain, and then
someone puts onto Ethereum a bridge contract. A bridge contract is
simply a contract that accepts block headers of the top chain, verifies
that any header submitted to it comes with a valid certificate showing
that it was accepted by the top chain's consensus, and adds that header
to a list. Applications can build on top of this to implement
functionality such as depositing and withdrawing tokens. Once such a
bridge is in place, does that provide any of the asset security
guarantees we mentioned earlier?
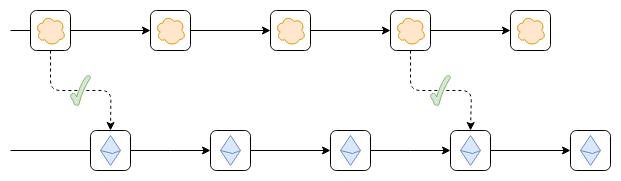
So far, not yet! For two reasons:
- We're validating that the blocks were signed, but not that
the state transitions are correct. Hence, if you have an asset issued on
Ethereum deposited to the top chain, and the top chain's validators go
rogue, they can sign an invalid state transition that steals those
assets.
- The top chain still has no way to read Ethereum. Hence, you
can't even deposit Ethereum-native assets onto the top chain without
relying on some other (possibly insecure) third-party bridge.
Now, let's make the bridge a validating bridge: it
checks not just consensus, but also a ZK-SNARK proving that the state of
any new block was computed correctly.
Once this is done, the top chain's validators can no longer steal
your funds. They can publish a block with unavailable data,
preventing everyone from withdrawing, but they cannot steal (except by
trying to extract a ransom for users in exchange for revealing the data
that allows them to withdraw). This is the same security model as a
validium.
However, we still have not solved the second problem: the top chain
cannot read Ethereum.
To do that, we need to do one of two things:
- Put a bridge contract validating finalized Ethereum blocks inside
the top chain.
- Have each block in the top chain contain a hash of a recent Ethereum
block, and have a fork choice rule that enforces the hash linkings. That
is, a top chain block that links to an Ethereum block that is not in the
canonical chain is itself non-canonical, and if a top chain block links
to an Ethereum block that was at first canonical, but then becomes
non-canonical, the top chain block must also become non-canonical.
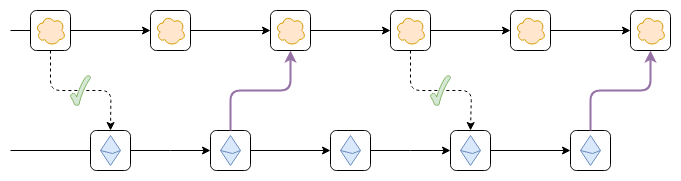
The purple links can be either hash links or a bridge contract
that verifies Ethereum's consensus.
Is this enough? As it turns out, still no, because of a few small
edge cases:
- What happens if Ethereum gets 51% attacked?
- How do you handle Ethereum hard fork upgrades?
- How do you handle hard fork upgrades of your chain?
A 51% attack on Ethereum would have similar consequences to a 51%
attack on the top chain, but in reverse. A hard fork of Ethereum risks
making the bridge of Ethereum inside the top chain no longer valid.
A social commitment to revert if Ethereum reverts a finalized
block, and to hard-fork if Ethereum hard-forks, is the cleanest way to
resolve this. Such a commitment may well never need to be
actually executed on: you could have a governance gadget on the top
chain activate if it sees proof of a possible attack or hard fork, and
only hard-fork the top chain if the governance gadget fails.
The only viable answer to (3) is, unfortunately, to have some form of
governance gadget on Ethereum that can make the bridge contract on
Ethereum aware of hard-fork upgrades of the top chain.
Summary: two-way validating bridges are
almost enough to make a chain a validium. The main remaining
ingredient is a social commitment that if something exceptional happens
in Ethereum that makes the bridge no longer work, the other chain will
hard-fork in response.
Conclusions
There are two key dimensions to "connectedness to Ethereum":
- Security of withdrawing to Ethereum
- Security of reading Ethereum
These are both important, and have different considerations. There is
a spectrum in both cases:
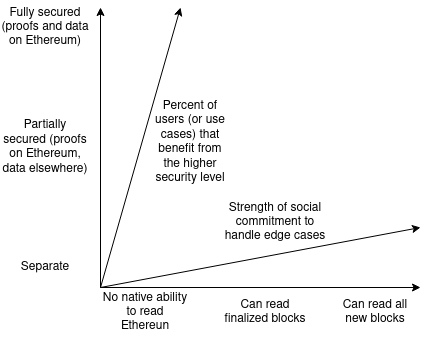
Notice that both dimensions each have two distinct ways of measuring
them (so really there's four dimensions?): security of
withdrawing can be measured by (i) security level, and (ii)
what percent of users or use cases benefit from the highest security
level, and security of reading can be measured by (i)
how quickly the chain can read Ethereum's blocks, particularly finalized
blocks vs any blocks, and (ii) the strength of the chain's social
commitment to handle edge cases such as 51% attacks and hard forks.
There is value in projects in many regions of this design space. For
some applications, high security and tight connectedness are important.
For others, something looser is acceptable in exhcnage for greater
scalability. In many cases, starting with something looser today, and
moving to a tighter coupling over the next decade as technology
improves, may well be optimal.
Different types of layer 2s
2023 Oct 31 See all postsSpecial thanks to Karl Floersch for feedback and review
The Ethereum layer 2 ecosystem has been expanding rapidly over the last year. The EVM rollup ecosystem, traditionally featuring Arbitrum, Optimism and Scroll, and more recently Kakarot and Taiko, has been progressing quickly, making great strides on improving their security; the L2beat page does a good job of summarizing the state of each project. Additionally, we have seen teams building sidechains also starting to build rollups (Polygon), layer 1 projects seeking to move toward being validiums (Celo), and totally new efforts (Linea, Zeth...). Finally, there is the not-just-EVM ecosystem: "almost-EVMs" like Zksync, extensions like Arbitrum Stylus, and broader efforts like the Starknet ecosystem, Fuel and others.
One of the inevitable consequences of this is that we are seeing a trend of layer 2 projects becoming more heterogeneous. I expect this trend to continue, for a few key reasons:
A big theme is that while applications and users that are on the Ethereum layer 1 today will be fine paying smaller but still visible rollup fees in the short term, users from the non-blockchain world will not: it's easier to justify paying $0.10 if you were paying $1 before than if you were paying $0 before. This applies both to applications that are centralized today, and to smaller layer 1s, which do typically have very low fees while their userbase remains small.
A natural question that emerges is: which of these complicated tradeoffs between rollups, validiums and other systems makes sense for a given application?
Rollups vs validiums vs disconnected systems
The first dimension of security vs scale that we will explore can be described as follows: if you have an asset that is issued on L1, then deposited into the L2, then transferred to you, what level of guarantee do you have that you will be able to take the asset back to the L1?
There is also a parallel question: what is the technology choice that is resulting in that level of guarantee, and what are the tradeoffs of that technology choice?
We can describe this simply using a chart:
It's worth mentioning that this is a simplified schema, and there are lots of intermediate options. For example:
These intermediate options can be viewed as being on a spectrum between a rollup and a validium. But what motivates applications to choose a particular point on that spectrum, and not some point further left or further right? Here, there are two major factors:
Approximately, this tradeoff looks something like this:
Another type of partial guarantee worth mentioning is pre-confirmations. Pre-confirmations are messages signed by some set of participants in a rollup or validium that say "we attest that these transactions are included in this order, and the post-state root is this". These participants may well sign a pre-confirmation that does not match some later reality, but if they do, a deposit gets burned. This is useful for low-value applications like consumer payments, while higher-value applications like multimillion-dollar financial transfers will likely wait for a "regular" confirmation backed by the system's full security.
Pre-confirmations can be viewed as another example of a hybrid system, similar to the "plasma / validium hybrid" mentioned above, but this time hybridizing between a rollup (or validium) that has full security but high latency, and a system with a much lower security level that has low latency. Applications that need lower latency get lower security, but can live in the same ecosystem as applications that are okay with higher latency in exchange for maximum security.
Trustlessly reading Ethereum
Another less-thought-about, but still highly important, form of connection has to do with a system's ability to read the Ethereum blockchain. Particularly, this includes being able to revert if Ethereum reverts. To see why this is valuable, consider the following situation:
Suppose that, as shown in the diagram, the Ethereum chain reverts. This could be a temporary hiccup within an epoch, while the chain has not finalized, or it could be an inactivity leak period where the chain is not finalizing for an extended duration because too many validators are offline.
The worst-case scenario that can arise from this is as follows. Suppose that the first block from the top chain reads some data from the leftmost block on the Ethereum chain. For example, someone on Ethereum deposits 100 ETH into the top chain. Then, Ethereum reverts. However, the top chain does not revert. As a result, future blocks of the top chain correctly follow new blocks from the newly correct Ethereum chain, but the consequences of the now-erroneous older link (namely, the 100 ETH deposit) are still part of the top chain. This exploit could allow printing money, turning the bridged ETH on the top chain into a fractional reserve.
There are two ways to solve this problem:
Note that (1) does have one edge case. If a 51% attack on Ethereum creates two new incompatible blocks that both appear finalized at the same time, then the top chain may well lock on to the wrong one (ie. the one that Ethereum social consensus does not eventually favor), and would have to revert to switch to the right one. Arguably, there is no need to write code to handle this case ahead of time; it could simply be handled by hard-forking the top chain.
The ability of a chain to trustlessly read Ethereum is valuable for two reasons:
Does having a bridge make you a validium?
Suppose that the top chain starts out as a separate chain, and then someone puts onto Ethereum a bridge contract. A bridge contract is simply a contract that accepts block headers of the top chain, verifies that any header submitted to it comes with a valid certificate showing that it was accepted by the top chain's consensus, and adds that header to a list. Applications can build on top of this to implement functionality such as depositing and withdrawing tokens. Once such a bridge is in place, does that provide any of the asset security guarantees we mentioned earlier?
So far, not yet! For two reasons:
Now, let's make the bridge a validating bridge: it checks not just consensus, but also a ZK-SNARK proving that the state of any new block was computed correctly.
Once this is done, the top chain's validators can no longer steal your funds. They can publish a block with unavailable data, preventing everyone from withdrawing, but they cannot steal (except by trying to extract a ransom for users in exchange for revealing the data that allows them to withdraw). This is the same security model as a validium.
However, we still have not solved the second problem: the top chain cannot read Ethereum.
To do that, we need to do one of two things:
The purple links can be either hash links or a bridge contract that verifies Ethereum's consensus.
Is this enough? As it turns out, still no, because of a few small edge cases:
A 51% attack on Ethereum would have similar consequences to a 51% attack on the top chain, but in reverse. A hard fork of Ethereum risks making the bridge of Ethereum inside the top chain no longer valid. A social commitment to revert if Ethereum reverts a finalized block, and to hard-fork if Ethereum hard-forks, is the cleanest way to resolve this. Such a commitment may well never need to be actually executed on: you could have a governance gadget on the top chain activate if it sees proof of a possible attack or hard fork, and only hard-fork the top chain if the governance gadget fails.
The only viable answer to (3) is, unfortunately, to have some form of governance gadget on Ethereum that can make the bridge contract on Ethereum aware of hard-fork upgrades of the top chain.
Summary: two-way validating bridges are almost enough to make a chain a validium. The main remaining ingredient is a social commitment that if something exceptional happens in Ethereum that makes the bridge no longer work, the other chain will hard-fork in response.
Conclusions
There are two key dimensions to "connectedness to Ethereum":
These are both important, and have different considerations. There is a spectrum in both cases:
Notice that both dimensions each have two distinct ways of measuring them (so really there's four dimensions?): security of withdrawing can be measured by (i) security level, and (ii) what percent of users or use cases benefit from the highest security level, and security of reading can be measured by (i) how quickly the chain can read Ethereum's blocks, particularly finalized blocks vs any blocks, and (ii) the strength of the chain's social commitment to handle edge cases such as 51% attacks and hard forks.
There is value in projects in many regions of this design space. For some applications, high security and tight connectedness are important. For others, something looser is acceptable in exhcnage for greater scalability. In many cases, starting with something looser today, and moving to a tighter coupling over the next decade as technology improves, may well be optimal.