On Path Independence
2017 Jun 22
See all posts
On Path Independence
Suppose that someone walks up to you and starts exclaiming to you
that he thinks he has figured out how to create a source of unlimited
free energy. His scheme looks as follows. First, you get a spaceship up
to low Earth orbit. There, Earth's gravity is fairly high, and so the
spaceship will start to accelerate heavily toward the earth. The
spaceship puts itself into a trajectory so that it barely brushes past
the Earth's atmosphere, and then keeps hurtling far into space. Further
in space, the gravity is lower, and so the spaceship can go higher
before it starts once again coming down. When it comes down, it takes a
curved path toward the Earth, so as to maximize its time in low orbit,
maximizing the acceleration it gets from the high gravity there, so that
after it passes by the Earth it goes even higher. After it goes high
enough, it flies through the Earth's atmosphere, slowing itself down but
using the waste heat to power a thermal reactor. Then, it would go back
to step one and keep going.
Something like this:
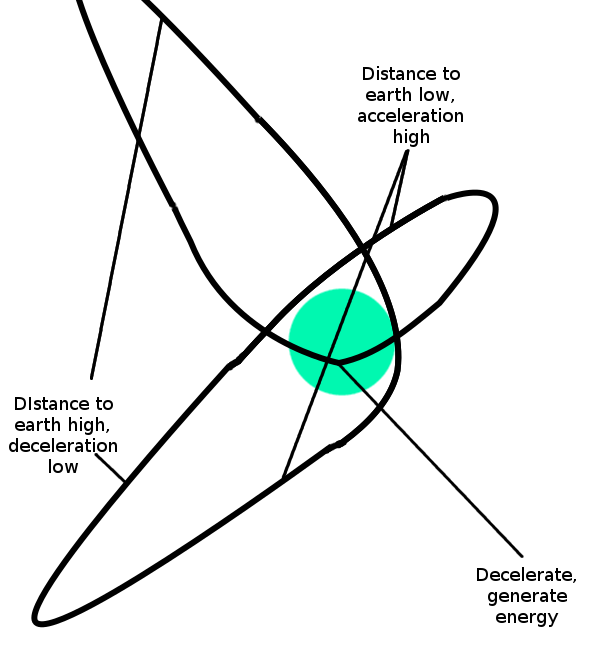
Now, if you know anything about Newtonian dynamics, chances are
you'll immediately recognize that this scheme is total bollocks. But how
do you know? You could make an appeal to symmetry, saying "look, for
every slice of the orbital path where you say gravity gives you high
acceleration, there's a corresponding slice of the orbital path where
gravity gives you just as high deceleration, so I don't see where the
net gains are coming from". But then, suppose the man presses you. "Ah,"
he says, "but in that slice where there is high acceleration your
initial velocity is low, and so you spend a lot of time inside of it,
whereas in the corresponding slice, your incoming velocity is high, and
so you have less time to decelerate". How do you really, conclusively,
prove him wrong?
One approach is to dig deeply into the math, calculate the integrals,
and show that the supposed net gains are in fact exactly equal to zero.
But there is also a simple approach: recognize that energy is
path-independent. That is, when the spaceship moves from point
\(A\) to point \(B\), where point \(B\) is closer to the earth, its kinetic
energy certainly goes up because its speed increases. But because total
energy (kinetic plus potential) is
conserved, and potential energy is only dependent on the spaceship's
position, and not how it got there, we know that regardless of
what path from point \(A\) to point
\(B\) the spaceship takes, once it gets
to point \(B\) the total change in
kinetic energy will be exactly the same.
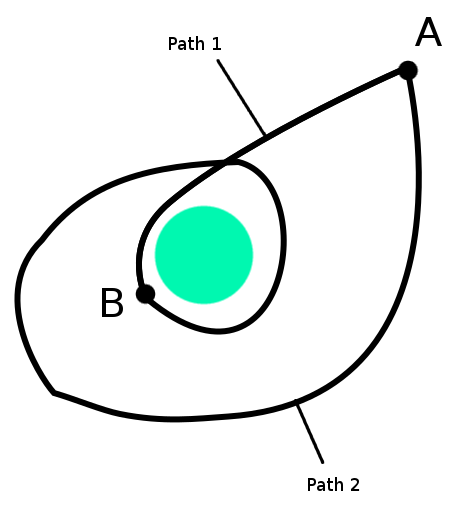
Different paths, same change in energy
Furthermore, we know that the kinetic energy gain from going
from point \(A\) to point \(A\) is also independent of the path
you take along the way: in all cases it's exactly zero.
One concern
sometimes cited
against on-chain market makers (that is, fully automated on-chain
mechanisms that act as always-available counterparties for people who
wish to trade one type of token for another) is that they are invariably
easy to exploit.
As an example, let me quote a recent
post discussing this issue in the context of Bancor:
The prices that Bancor offers for tokens have nothing to do with the
actual market equilibrium. Bancor will always trail the market, and in
doing so, will bleed its reserves. A simple thought experiment suffices
to illustrate the problem. Suppose that market panic sets around X.
Unfounded news about your system overtake social media. Let's suppose
that people got convinced that your CEO has absconded to a remote island
with no extradition treaty, that your CFO has been embezzling money, and
your CTO was buying drugs from the darknet markets and shipping them to
his work address to make a Scarface-like mound of white powder on his
desk. Worse, let's suppose that you know these allegations to be false.
They were spread by a troll army wielded by a company with no products,
whose business plan is to block everyone's coin stream. Bancor would
offer ever decreasing prices for X coins during a bank run, until it has
no reserves left. You'd watch the market panic take hold and eat away
your reserves. Recall that people are convinced that the true value of X
is 0 in this scenario, and the Bancor formula is guaranteed to offer a
price above that. So your entire reserve would be gone.
The post discusses many issues around the Bancor protocol, including
details such as code quality, and I will not touch on any of those;
instead, I will focus purely on the topic of on-chain market maker
efficiency and exploitability, using Bancor (along with MKR) purely as
examples and not seeing to make any judgements on the quality of either
project as a whole.
For many classes of naively designed on-chain market makers, the
comment above about exploitability and trailing markets applies
verbatim, and quite seriously so. However, there are also classes of
on-chain market makers that are definitely not suspect to their entire
reserve being drained due to some kind of money-pumping attack. To take
a simple example, consider the market maker selling MKR for ETH whose
internal state consists of a current price, \(p\), and which is willing to buy or sell an
infinitesimal amount of MKR at each price level. For example, suppose
that \(p = 5\), and you wanted to buy 2
MKR. The market would sell you:
- 0.00...01 MKR at a price of 5 ETH/MKR
- 0.00...01 MKR at a price of 5.00...01 ETH/MKR
- 0.00...01 MKR at a price of 5.00...02 ETH/MKR
- ....
- 0.00...01 MKR at a price of 6.99...98 ETH/MKR
- 0.00...01 MKR at a price of 6.99...99 ETH/MKR
Altogether, it's selling you 2 MKR at an average price of 6 ETH/MKR
(ie. total cost 12 ETH), and at the end of the operation \(p\) has increased to 7. If someone
then wanted to sell 1 MKR, they would be spending 6.5 ETH, and
at the end of that operation \(p\) would drop back down to 6.
Now, suppose that I told you that such a market maker started off at
a price of \(p = 5\), and after an
unspecified series of events \(p\) is
now 4. Two questions:
- How much MKR did the market maker gain or lose?
- How much ETH did the market maker gain or lose?
The answers are: it gained 1 MKR, and lost 4.5 ETH. Notice that this
result is totally independent of the path that \(p\) took. Those answers are correct if
\(p\) went from 5 to 4 directly with
one buyer, they're correct if there was first one buyer that took \(p\) from 5 to 4.7 and a second buyer that
took \(p\) the rest of the way to 4,
and they're even correct if \(p\) first
dropped to 2, then increased to 9.818, then dropped again to 0.53, then
finally rose again to 4.
Why is this the case? The simplest way to see this is to see that if
\(p\) drops below 4 and then comes back
up to 4, the sells on the way down are exactly counterbalanced by buys
on the way up; each sell has a corresponding buy of the same magnitude
at the exact same price. But we can also see this by viewing the market
maker's core mechanism differently. Define the market maker as having a
single-dimensional internal state \(p\), and having MKR and ETH balances
defined by the following formulas:
\(mkr\_balance(p) = 10 - p\)
\(eth\_balance(p) = p^2/2\)
Anyone has the power to "edit" \(p\)
(though only to values between 0 and 10), but they can only do so by
supplying the right amount of MKR or ETH, and getting the right amount
of MKR and ETH back, so that the balances still match up; that is, so
that the amount of MKR and ETH held by the market maker after the
operation is the amount that they are supposed to hold according to the
above formulas, with the new value for \(p\) that was set. Any edit to \(p\) that does not come with MKR and ETH
transactions that make the balances match up automatically fails.
Now, the fact that any series of events that drops \(p\) from 5 to 4 also raises the market
maker's MKR balance by 1 and drops its ETH balance by 4.5, regardless of
what series of events it was, should look elementary: \(mkr\_balance(4) - mkr\_balance(5) = 1\) and
\(eth\_balance(4) - eth\_balance(5) =
-4.5\).
What this means is that a "reserve bleeding" attack on a market maker
that preserves this kind of path independence property is impossible.
Even if some trolls successfully create a market panic that drops prices
to near-zero, when the panic subsides, and prices return to their
original levels, the market maker's position will be unchanged - even if
both the price, and the market maker's balances, made a bunch of crazy
moves in the meantime.
Now, this does not mean that market makers cannot lose money,
compared to other holding strategies. If, when you start off, 1 MKR = 5
ETH, and then the MKR price moves, and we compare the performance of
holding 5 MKR and 12.5 ETH in the market maker versus the performance of
just holding the assets, the result looks like this:
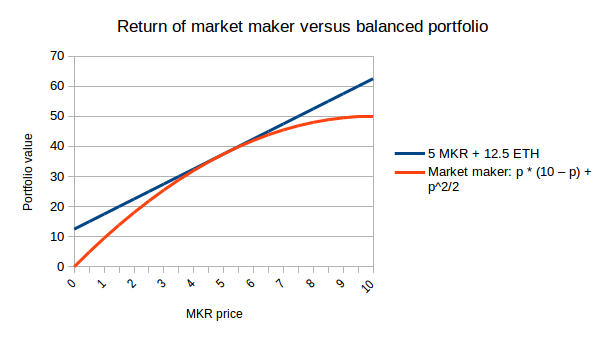
Holding a balanced portfolio always wins, except in the case where
prices stay exactly the same, in which case the returns of the market
maker and the balanced portfolio are equal. Hence, the purpose of a
market maker of this type is to subsidize guaranteed liquidity as a
public good for users, serving as trader of last resort, and not to earn
revenue. However, we certainly can modify the market maker to earn
revenue, and quite simply: we have it charge a spread. That is, the
market maker might charge \(1.005\cdot
p\) for buys and offer only \(0.995\cdot p\) for sells. Now, being the
beneficiary of a market maker becomes a bet: if, in the long run, prices
tend to move in one direction, then the market maker loses, at least
relative to what they could have gained if they had a balanced
portfolio. If, on the other hand, prices tend to bounce around wildly
but ultimately come back to the same point, then the market maker can
earn a nice profit. This sacrifices the "path independence" property,
but in such a way that any deviations from path independence are always
in the market maker's favor.
There are many designs that path-independent market makers could
take; if you are willing to create a token that can issue an unlimited
quantity of units, then the "constant reserve ratio" mechanism (where
for some constant ratio \(0 \leq r \leq
1\), the token supply is \(p^{1/r -
1}\) and the reserve size is \(r \cdot
p^{1/r}\) also counts as one, provided that it is implemented
correctly and path independence is not compromised by bounds and
rounding errors.
If you want to make a market maker for existing tokens without a
price cap, my favorite (credit to Martin Koppelmann) mechanism is that
which maintains the invariant \(tokenA\_balance(p) \cdot tokenB\_balance(p) =
k\) for some constant \(k\). So
the formulas would be:
\(tokenA\_balance(p) = \sqrt{k\cdot
p}\)
\(tokenB\_balance(p) =
\sqrt{k/p}\)
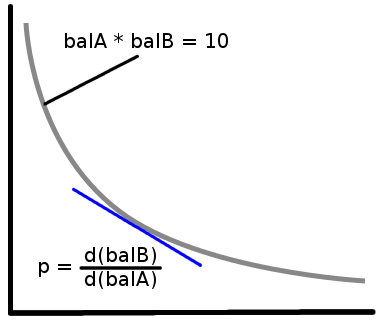
Where \(p\) is the price of \(tokenB\) denominated in \(tokenA\). In general, you can make a
path-independent market maker by defining any (monotonic) relation
between \(tokenA\_balance\) and \(tokenB\_balance\) and calculating its
derivative at any point to give the price.
The above only discusses the role of path independence in
preventing one particular type of issue: that where an attacker somehow
makes a series of transactions in the context of a series of price
movements in order to repeatedly drain the market maker of money. With a
path independent market maker, such "money pump" vulnerabilities are
impossible. However, there certainly are other kinds of
inefficiencies that may exist. If the price of MKR drops from 5 ETH to 1
ETH, then the market maker used in the example above will have lost 28
ETH worth of value, whereas a balanced portfolio would only have lost 20
ETH. Where did that 8 ETH go?
In the best case, the price (that is to say, the "real" price, the
price level where supply and demand among all users and traders matches
up) drops quickly, and some lucky trader snaps up the deal, claiming an
8 ETH profit minus negligible transaction fees. But what if there are
multiple traders? Then, if the price between block \(n\) and block \(n+1\) differs, the fact that traders can
bid against each other by setting transaction fees creates an all-pay
auction, with revenues going to the miner. As a consequence of the revenue
equivalence theorem, we can deduce that we can expect that the
transaction fees that traders send into this mechanism will keep going
up until they are roughly equal to the size of the profit earned (at
least initially; the real equilibrium is for miners to just
snap up the money themselves). Hence, either way schemes like this are
ultimately a gift to the miners.
One way to increase social welfare in such a design is to make it
possible to create purchase transactions that are only worthwhile for
miners to include if they actually make the purchase. That is, if the
"real" price of MKR falls from 5 to 4.9, and there are 50 traders racing
to arbitrage the market maker, and only the first one of those 50 will
make the trade, then only that one should pay the miner a transaction
fee. This way, the other 49 failed trades will not clog up the
blockchain. EIP
86, slated for Metropolis, opens up a path toward standardizing such
a conditional transaction fee mechanism (another good side effect is
that this can also make token sales more unobtrusive, as similar
all-pay-auction mechanics apply in many token sales).
Additionally, there are other inefficiencies if the market maker is
the only available trading venue for tokens. For example, if
two traders want to exchange a large amount, then they would need to do
so via a long series of small buy and sell transactions, needlessly
clogging up the blockchain. To mitigate such efficiencies, an on-chain
market maker should only be one of the trading venues
available, and not the only one. However, this is arguably not a large
concern for protocol developers; if there ends up being a demand for a
venue for facilitating large-scale trades, then someone else will likely
provide it.
Furthermore, the arguments here only talk about path independence of
the market maker assuming a given starting price and ending
price. However, because of various psychological effects, as well as
multi-equilibrium effects, the ending price is plausibly a function not
just of the starting price and recent events that affect the
"fundamental" value of the asset, but also of the pattern of trades that
happens in response to those events. If a price-dropping event takes
place, and because of poor liquidity the price of the asset drops
quickly, it may end up recovering to a lower point than if more
liquidity had been present in the first place. That said, this may
actually be an argument in favor of subsidied market makers: if such
multiplier effects exist, then they will have a positive impact on price
stability that goes beyond the first-order effect of the liquidity that
the market maker itself provides.
There is likely a lot of research to be done in determining exactly
which path-independent market maker is optimal. There is also the
possibility of hybrid semi-automated market makers that have the same
guaranteed-liquidity properties, but which include some element of
asynchrony, as well as the ability for the operator to "cut in line" and
collect the profits in cases where large amounts of capital would
otherwise be lost to miners. There is also not yet a coherent theory of
just how much (if any) on-chain automated guaranteed liquidity is
optimal for various objectives, and to what extent, and by whom, these
market makers should be subsidized. All in all, the on-chain mechanism
design space is still in its early days, and it's certainly worth much
more broadly researching and exploring various options.
On Path Independence
2017 Jun 22 See all postsSuppose that someone walks up to you and starts exclaiming to you that he thinks he has figured out how to create a source of unlimited free energy. His scheme looks as follows. First, you get a spaceship up to low Earth orbit. There, Earth's gravity is fairly high, and so the spaceship will start to accelerate heavily toward the earth. The spaceship puts itself into a trajectory so that it barely brushes past the Earth's atmosphere, and then keeps hurtling far into space. Further in space, the gravity is lower, and so the spaceship can go higher before it starts once again coming down. When it comes down, it takes a curved path toward the Earth, so as to maximize its time in low orbit, maximizing the acceleration it gets from the high gravity there, so that after it passes by the Earth it goes even higher. After it goes high enough, it flies through the Earth's atmosphere, slowing itself down but using the waste heat to power a thermal reactor. Then, it would go back to step one and keep going.
Something like this:
Now, if you know anything about Newtonian dynamics, chances are you'll immediately recognize that this scheme is total bollocks. But how do you know? You could make an appeal to symmetry, saying "look, for every slice of the orbital path where you say gravity gives you high acceleration, there's a corresponding slice of the orbital path where gravity gives you just as high deceleration, so I don't see where the net gains are coming from". But then, suppose the man presses you. "Ah," he says, "but in that slice where there is high acceleration your initial velocity is low, and so you spend a lot of time inside of it, whereas in the corresponding slice, your incoming velocity is high, and so you have less time to decelerate". How do you really, conclusively, prove him wrong?
One approach is to dig deeply into the math, calculate the integrals, and show that the supposed net gains are in fact exactly equal to zero. But there is also a simple approach: recognize that energy is path-independent. That is, when the spaceship moves from point \(A\) to point \(B\), where point \(B\) is closer to the earth, its kinetic energy certainly goes up because its speed increases. But because total energy (kinetic plus potential) is conserved, and potential energy is only dependent on the spaceship's position, and not how it got there, we know that regardless of what path from point \(A\) to point \(B\) the spaceship takes, once it gets to point \(B\) the total change in kinetic energy will be exactly the same.
Different paths, same change in energy
Furthermore, we know that the kinetic energy gain from going from point \(A\) to point \(A\) is also independent of the path you take along the way: in all cases it's exactly zero.
One concern sometimes cited against on-chain market makers (that is, fully automated on-chain mechanisms that act as always-available counterparties for people who wish to trade one type of token for another) is that they are invariably easy to exploit.
As an example, let me quote a recent post discussing this issue in the context of Bancor:
The post discusses many issues around the Bancor protocol, including details such as code quality, and I will not touch on any of those; instead, I will focus purely on the topic of on-chain market maker efficiency and exploitability, using Bancor (along with MKR) purely as examples and not seeing to make any judgements on the quality of either project as a whole.
For many classes of naively designed on-chain market makers, the comment above about exploitability and trailing markets applies verbatim, and quite seriously so. However, there are also classes of on-chain market makers that are definitely not suspect to their entire reserve being drained due to some kind of money-pumping attack. To take a simple example, consider the market maker selling MKR for ETH whose internal state consists of a current price, \(p\), and which is willing to buy or sell an infinitesimal amount of MKR at each price level. For example, suppose that \(p = 5\), and you wanted to buy 2 MKR. The market would sell you:
Altogether, it's selling you 2 MKR at an average price of 6 ETH/MKR (ie. total cost 12 ETH), and at the end of the operation \(p\) has increased to 7. If someone then wanted to sell 1 MKR, they would be spending 6.5 ETH, and at the end of that operation \(p\) would drop back down to 6.
Now, suppose that I told you that such a market maker started off at a price of \(p = 5\), and after an unspecified series of events \(p\) is now 4. Two questions:
The answers are: it gained 1 MKR, and lost 4.5 ETH. Notice that this result is totally independent of the path that \(p\) took. Those answers are correct if \(p\) went from 5 to 4 directly with one buyer, they're correct if there was first one buyer that took \(p\) from 5 to 4.7 and a second buyer that took \(p\) the rest of the way to 4, and they're even correct if \(p\) first dropped to 2, then increased to 9.818, then dropped again to 0.53, then finally rose again to 4.
Why is this the case? The simplest way to see this is to see that if \(p\) drops below 4 and then comes back up to 4, the sells on the way down are exactly counterbalanced by buys on the way up; each sell has a corresponding buy of the same magnitude at the exact same price. But we can also see this by viewing the market maker's core mechanism differently. Define the market maker as having a single-dimensional internal state \(p\), and having MKR and ETH balances defined by the following formulas:
\(mkr\_balance(p) = 10 - p\)
\(eth\_balance(p) = p^2/2\)
Anyone has the power to "edit" \(p\) (though only to values between 0 and 10), but they can only do so by supplying the right amount of MKR or ETH, and getting the right amount of MKR and ETH back, so that the balances still match up; that is, so that the amount of MKR and ETH held by the market maker after the operation is the amount that they are supposed to hold according to the above formulas, with the new value for \(p\) that was set. Any edit to \(p\) that does not come with MKR and ETH transactions that make the balances match up automatically fails.
Now, the fact that any series of events that drops \(p\) from 5 to 4 also raises the market maker's MKR balance by 1 and drops its ETH balance by 4.5, regardless of what series of events it was, should look elementary: \(mkr\_balance(4) - mkr\_balance(5) = 1\) and \(eth\_balance(4) - eth\_balance(5) = -4.5\).
What this means is that a "reserve bleeding" attack on a market maker that preserves this kind of path independence property is impossible. Even if some trolls successfully create a market panic that drops prices to near-zero, when the panic subsides, and prices return to their original levels, the market maker's position will be unchanged - even if both the price, and the market maker's balances, made a bunch of crazy moves in the meantime.
Now, this does not mean that market makers cannot lose money, compared to other holding strategies. If, when you start off, 1 MKR = 5 ETH, and then the MKR price moves, and we compare the performance of holding 5 MKR and 12.5 ETH in the market maker versus the performance of just holding the assets, the result looks like this:
Holding a balanced portfolio always wins, except in the case where prices stay exactly the same, in which case the returns of the market maker and the balanced portfolio are equal. Hence, the purpose of a market maker of this type is to subsidize guaranteed liquidity as a public good for users, serving as trader of last resort, and not to earn revenue. However, we certainly can modify the market maker to earn revenue, and quite simply: we have it charge a spread. That is, the market maker might charge \(1.005\cdot p\) for buys and offer only \(0.995\cdot p\) for sells. Now, being the beneficiary of a market maker becomes a bet: if, in the long run, prices tend to move in one direction, then the market maker loses, at least relative to what they could have gained if they had a balanced portfolio. If, on the other hand, prices tend to bounce around wildly but ultimately come back to the same point, then the market maker can earn a nice profit. This sacrifices the "path independence" property, but in such a way that any deviations from path independence are always in the market maker's favor.
There are many designs that path-independent market makers could take; if you are willing to create a token that can issue an unlimited quantity of units, then the "constant reserve ratio" mechanism (where for some constant ratio \(0 \leq r \leq 1\), the token supply is \(p^{1/r - 1}\) and the reserve size is \(r \cdot p^{1/r}\) also counts as one, provided that it is implemented correctly and path independence is not compromised by bounds and rounding errors.
If you want to make a market maker for existing tokens without a price cap, my favorite (credit to Martin Koppelmann) mechanism is that which maintains the invariant \(tokenA\_balance(p) \cdot tokenB\_balance(p) = k\) for some constant \(k\). So the formulas would be:
\(tokenA\_balance(p) = \sqrt{k\cdot p}\)
\(tokenB\_balance(p) = \sqrt{k/p}\)
Where \(p\) is the price of \(tokenB\) denominated in \(tokenA\). In general, you can make a path-independent market maker by defining any (monotonic) relation between \(tokenA\_balance\) and \(tokenB\_balance\) and calculating its derivative at any point to give the price.
The above only discusses the role of path independence in preventing one particular type of issue: that where an attacker somehow makes a series of transactions in the context of a series of price movements in order to repeatedly drain the market maker of money. With a path independent market maker, such "money pump" vulnerabilities are impossible. However, there certainly are other kinds of inefficiencies that may exist. If the price of MKR drops from 5 ETH to 1 ETH, then the market maker used in the example above will have lost 28 ETH worth of value, whereas a balanced portfolio would only have lost 20 ETH. Where did that 8 ETH go?
In the best case, the price (that is to say, the "real" price, the price level where supply and demand among all users and traders matches up) drops quickly, and some lucky trader snaps up the deal, claiming an 8 ETH profit minus negligible transaction fees. But what if there are multiple traders? Then, if the price between block \(n\) and block \(n+1\) differs, the fact that traders can bid against each other by setting transaction fees creates an all-pay auction, with revenues going to the miner. As a consequence of the revenue equivalence theorem, we can deduce that we can expect that the transaction fees that traders send into this mechanism will keep going up until they are roughly equal to the size of the profit earned (at least initially; the real equilibrium is for miners to just snap up the money themselves). Hence, either way schemes like this are ultimately a gift to the miners.
One way to increase social welfare in such a design is to make it possible to create purchase transactions that are only worthwhile for miners to include if they actually make the purchase. That is, if the "real" price of MKR falls from 5 to 4.9, and there are 50 traders racing to arbitrage the market maker, and only the first one of those 50 will make the trade, then only that one should pay the miner a transaction fee. This way, the other 49 failed trades will not clog up the blockchain. EIP 86, slated for Metropolis, opens up a path toward standardizing such a conditional transaction fee mechanism (another good side effect is that this can also make token sales more unobtrusive, as similar all-pay-auction mechanics apply in many token sales).
Additionally, there are other inefficiencies if the market maker is the only available trading venue for tokens. For example, if two traders want to exchange a large amount, then they would need to do so via a long series of small buy and sell transactions, needlessly clogging up the blockchain. To mitigate such efficiencies, an on-chain market maker should only be one of the trading venues available, and not the only one. However, this is arguably not a large concern for protocol developers; if there ends up being a demand for a venue for facilitating large-scale trades, then someone else will likely provide it.
Furthermore, the arguments here only talk about path independence of the market maker assuming a given starting price and ending price. However, because of various psychological effects, as well as multi-equilibrium effects, the ending price is plausibly a function not just of the starting price and recent events that affect the "fundamental" value of the asset, but also of the pattern of trades that happens in response to those events. If a price-dropping event takes place, and because of poor liquidity the price of the asset drops quickly, it may end up recovering to a lower point than if more liquidity had been present in the first place. That said, this may actually be an argument in favor of subsidied market makers: if such multiplier effects exist, then they will have a positive impact on price stability that goes beyond the first-order effect of the liquidity that the market maker itself provides.
There is likely a lot of research to be done in determining exactly which path-independent market maker is optimal. There is also the possibility of hybrid semi-automated market makers that have the same guaranteed-liquidity properties, but which include some element of asynchrony, as well as the ability for the operator to "cut in line" and collect the profits in cases where large amounts of capital would otherwise be lost to miners. There is also not yet a coherent theory of just how much (if any) on-chain automated guaranteed liquidity is optimal for various objectives, and to what extent, and by whom, these market makers should be subsidized. All in all, the on-chain mechanism design space is still in its early days, and it's certainly worth much more broadly researching and exploring various options.